Side Effects: What They Look Like and What You Should Do
Side effects are any unwanted changes that happen after you take a medicine. Some are mild and short-lived, like a headache or upset stomach. Others can be serious and need urgent care, like trouble breathing, chest pain, or sudden severe rash. Knowing the difference and acting fast keeps you safer.
Common types and timing
Side effects show up in different ways. Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, diarrhea), headaches, dizziness, sleep changes, and mild rashes are common. Some drugs cause specific problems: insulin can lead to low blood sugar, certain bone drugs may upset the stomach, and some antivirals can cause fatigue or nausea. Reactions can be immediate (minutes to hours), early (days), or delayed (weeks or months).
Watch how quickly symptoms appear after starting a new drug or changing dose. If something starts right after a medication change, treat that as a clue. Keep a short log: drug name, dose, start date, and any new symptoms. That helps your prescriber connect the dots fast.
Practical steps if you notice side effects
If you get mild symptoms, check the patient leaflet and call your prescriber or pharmacist. Don’t stop prescription meds suddenly without guidance—stopping some drugs abruptly can be risky. If symptoms are bothersome but not life-threatening, your doctor may change the dose, switch drugs, or suggest ways to manage side effects.
For severe signs—shortness of breath, swelling of face or throat, fainting, chest pain, high fever, yellowing skin or eyes—seek emergency care immediately. Say the drug name and when you took it. If possible, bring the medication bottle or a photo of the label.
Report serious or unexpected side effects to your national health authority (for example, FDA MedWatch in the U.S. or Health Canada’s adverse reaction reporting). Reporting helps catch safety issues early and protects others.
Buying medicines online? Be cautious. Counterfeit or mislabeled drugs raise the risk of unexpected side effects. Use licensed pharmacies that require a prescription, show clear contact info, and have real customer service. Look for consistent product info and compare the leaflet to trusted sources.
Practical tips: keep an up-to-date list of all meds and supplements, share it with every prescriber, and ask about drug interactions. When starting a new drug, ask what side effects are most likely, which ones need urgent attention, and how long they usually last. If a medicine makes daily life worse, tell your provider—there are often safer alternatives or dose adjustments.
Side effects are unpleasant, but they’re often manageable when spotted early. Be your own advocate: read labels, track symptoms, ask questions, and report serious reactions. That simple routine cuts risk and helps you get the treatment you need with fewer surprises.
Cephalexin (Keftab) vs. Common Antibiotic Alternatives: A Practical Comparison
A detailed, human-friendly comparison of Cephalexin (Keftab) with five common antibiotic alternatives, covering usage, side effects, cost, and when to choose each.

Temovate (Clobetasol Propionate) Guide: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects & Cost
A clear, up‑to‑date guide on Temovate: what it treats, how to use it, common side effects, safety tips and current pricing options for Canadian patients.

Finding the Best Mebendazole Deals: Effective Antiparasitic Options
Mebendazole, a powerful antiparasitic drug, is commonly used to treat various worm infections. It works by inhibiting the worm's ability to produce glucose, leading to their eventual death. Despite its efficacy, understanding the right dosage, potential side effects, and possible drug interactions is crucial for safe use. This article sheds light on these aspects while guiding readers to find the best Mebendazole deals available.
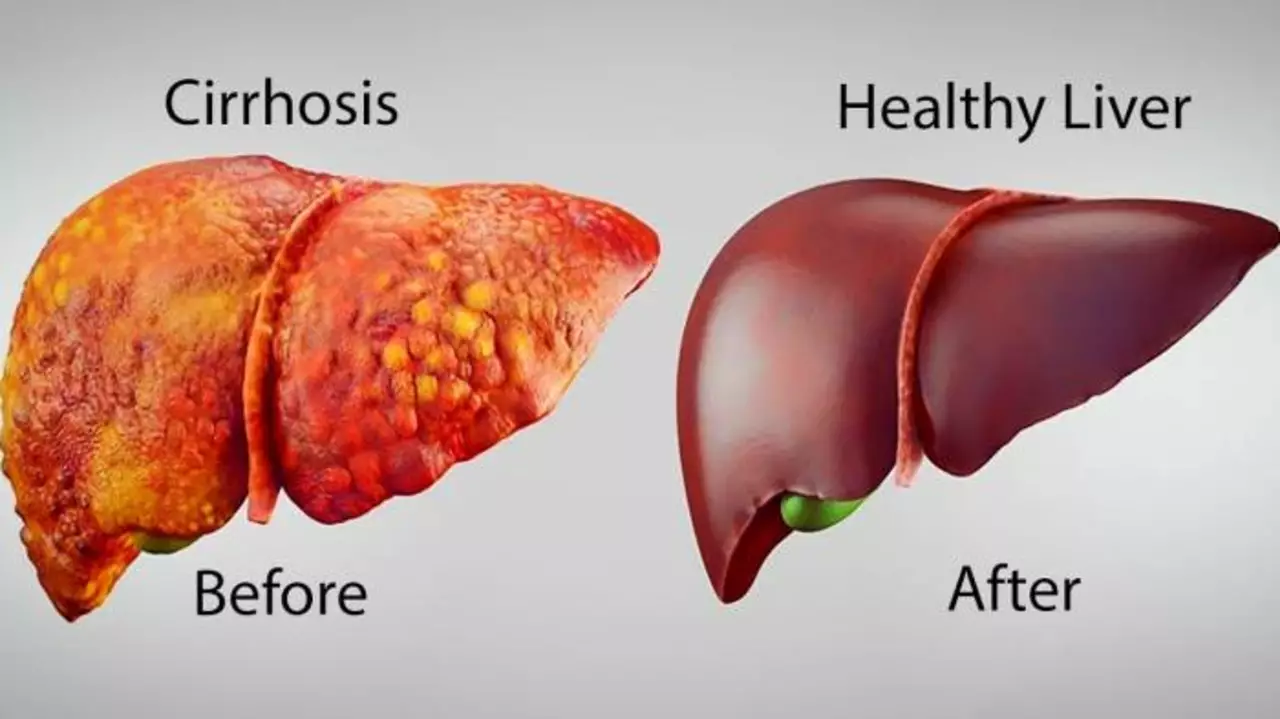
Primaquine and liver health: What you need to know
As a blogger, I feel it's essential to share vital information about Primaquine and liver health. Primaquine is an effective medication used to treat and prevent malaria, but it's crucial to be aware of its potential impact on liver health. Some individuals may experience liver damage due to a deficiency in G6PD, an enzyme that protects red blood cells. Therefore, it's important to get tested for G6PD deficiency before taking Primaquine to avoid any possible complications. Always remember to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure the best course of action for your specific situation.
Categories
- Medications (71)
- Health and Medicine (62)
- Health and Wellness (37)
- Online Pharmacy Guides (16)
- Nutrition and Supplements (9)
- Parenting and Family (3)
- Environment and Conservation (2)
- healthcare (2)
- prescription savings (1)
Popular Articles



