Primaquine and liver health: What you need to know
Introduction to Primaquine and Liver Health
As someone who's always been interested in maintaining a healthy lifestyle, I've come across various medications and supplements that can have an impact on our overall well-being. One such drug that caught my attention is Primaquine, an antimalarial medication that has been in use for many years. In this article, I will be discussing the relationship between Primaquine and liver health, exploring the potential benefits and risks associated with its use.
Understanding Primaquine: What is it and How Does it Work?
Primaquine is an antimalarial drug that has been used since the 1950s to treat and prevent malaria, a life-threatening disease caused by parasites transmitted through mosquito bites. It belongs to a class of drugs called 8-aminoquinolines and works by interfering with the growth and reproduction of the malaria-causing parasites in the body. As a result, the parasites are unable to multiply and cause disease, allowing the immune system to eliminate them.
In addition to treating malaria, Primaquine is also used as a prophylactic medication, meaning that it can be taken to prevent malaria in individuals traveling to areas where the disease is prevalent. This is particularly important for those who may be at higher risk for complications, such as pregnant women, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
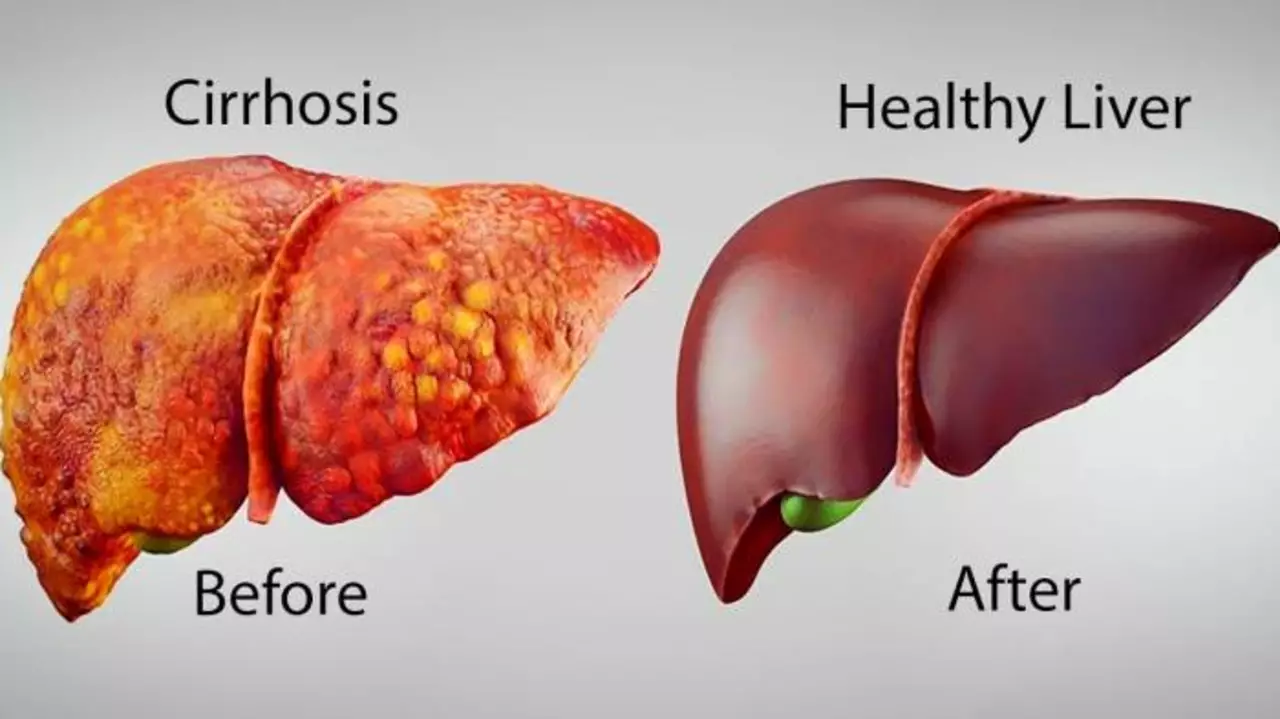
Primaquine and Liver Health: The Connection
So, how does Primaquine relate to liver health? The liver plays a crucial role in processing and metabolizing medications, including Primaquine. When the drug is taken, it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and then transported to the liver, where it undergoes biotransformation. This process converts the drug into its active form, which can then be distributed throughout the body to target the malaria-causing parasites.
Because the liver is responsible for metabolizing Primaquine, it is important to be aware of the potential impact that the drug can have on liver function. In some cases, Primaquine use can lead to liver toxicity, which can have serious implications for overall health.
Recognizing the Signs of Primaquine-Induced Liver Toxicity
While Primaquine-induced liver toxicity is relatively rare, it is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate a problem. Some of the most common symptoms of liver toxicity include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
If you experience any of these symptoms while taking Primaquine, it is crucial to consult your healthcare provider immediately. They can assess your liver function and determine whether any adjustments to your medication regimen are necessary.
Who is at Risk for Primaquine-Induced Liver Toxicity?
While anyone taking Primaquine can potentially develop liver toxicity, certain individuals may be at higher risk. These can include people with:
- Pre-existing liver disease or damage
- Alcohol abuse
- Concurrent use of other medications that can also cause liver toxicity
- Genetic predispositions to liver problems
It is essential for individuals at higher risk for Primaquine-induced liver toxicity to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their liver function and ensure that the drug is used safely and effectively.
Preventing and Managing Primaquine-Induced Liver Toxicity
Fortunately, there are several strategies that can be employed to help prevent and manage Primaquine-induced liver toxicity. These include:
- Working closely with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of Primaquine treatment
- Regularly monitoring liver function through blood tests
- Avoiding alcohol and other substances that can cause liver damage
- Being aware of potential drug interactions and discussing them with your healthcare provider
- Seeking medical attention promptly if you experience any symptoms of liver toxicity
Primaquine Alternatives: Other Antimalarial Options
If you are concerned about the potential risks associated with Primaquine and liver health, there are other antimalarial medications that may be more appropriate for your specific needs. Some of these alternatives include:
- Chloroquine
- Mefloquine
- Atovaquone-proguanil
- Doxycycline
Be sure to discuss your concerns and any pre-existing conditions with your healthcare provider, who can help you determine the best antimalarial medication for your situation.
Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Primaquine
While Primaquine is an effective treatment and prevention option for malaria, it is essential to be aware of the potential impact it can have on liver health. By knowing the signs of liver toxicity, understanding the risk factors, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can minimize the risks associated with Primaquine use and ensure that it is used safely and effectively.





Hannah Dawson
May 4, 2023 AT 23:23Reading through the Primaquine piece, I couldn't help but notice the way the author glosses over the prevalence of hepatic monitoring in real‑world practice. The data on drug‑induced liver injury is thin, yet the article throws out a laundry list of rare side effects as if they were common. In my experience, most clinicians rely on baseline LFTs and then only chase a problem when symptoms appear, which can delay detection. Moreover, the piece fails to address the variability in metabolic enzymes among different ethnic groups, a factor that can dramatically alter toxicity risk. The author mentions genetic predispositions but never cites any pharmacogenomic studies. This lack of depth raises questions about the thoroughness of the research. The article would benefit from a table summarizing risk factors alongside recommended monitoring intervals. Also, there's no discussion about how co‑administration with other antimalarials can potentiate hepatic stress. Overall, the piece feels like a surface‑level overview rather than an evidence‑based guide.
Julie Gray
May 4, 2023 AT 23:26One must consider the hidden agendas behind the promotion of Primaquine; its widespread endorsement by global health agencies conveniently aligns with certain pharmaceutical interests that thrive on the continued prevalence of malaria in developing regions. The omission of any discourse on the strategic manipulation of drug‑regulatory pathways suggests a deliberate veil over the true scope of hepatic complications that remain under‑reported. It is plausible that adverse event data are being suppressed to maintain a steady supply chain for profit motives. The reader should remain vigilant and question the provenance of the cited studies, which appear instead to be curated by entities with vested interests.
Lisa Emilie Ness
May 4, 2023 AT 23:30I appreciate the clear layout of risk factors and monitoring advice but would prefer a bit more concise wording.
Emily Wagner
May 4, 2023 AT 23:36The discourse on Primaquine invokes a broader philosophical contemplation of pharmaceutical intervention as a dialectic between human autonomy and biochemical determinism. In the ontological realm, the liver serves not merely as a metabolic organ but as a symbolic crucible wherein xenobiotics are transmuted, reflecting the tension between external agents and internal equilibrium. When Primaquine enters this system, it initiates a cascade of enzymatic negotiations that echo the Hegelian synthesis of thesis and antithesis; the drug's antimalarial potency constitutes the thesis, while hepatic stress embodies the antithesis, culminating in a precarious synthesis of therapeutic benefit and potential harm. Moreover, the stochastic nature of genetic polymorphisms introduces an element of indeterminacy reminiscent of quantum uncertainty, emphasizing that risk cannot be universally quantified. The article's enumeration of symptoms such as jaundice and fatigue, while clinically pertinent, also metaphorically signals the body's communicative distress signals, analogous to a language that the liver speaks when overwhelmed. It is essential to recognize that monitoring strategies are not merely procedural checkboxes but act as interpretive frameworks, enabling clinicians to decode these biochemical narratives. By integrating pharmacogenomic insights, we can refine this dialogue, reducing the epistemic gap between drug action and hepatic response. Ultimately, the balance of Primaquine's utility versus its hepatic risks underscores a profound ethical calculus: the moral imperative to alleviate malaria must be weighed against the duty to safeguard hepatic integrity, a decision matrix that demands both empirical rigor and philosophical humility.
Mark French
May 4, 2023 AT 23:43It is commendable that the author emphasizes regular liver function testing; patients often underestimate the importance of such follow‑ups and can benefit from a structured monitoring plan.
Daylon Knight
May 4, 2023 AT 23:46Sure, because we all love drinking booze while on a liver‑toxic drug, right?
Jason Layne
May 4, 2023 AT 23:53The so‑called "safety" of Primaquine is a myth perpetuated by a collusion of pharma lobbyists and complacent health organizations. Anyone who trusts the official narrative is either willfully ignorant or complicit in a massive cover‑up. The article fails to mention the clandestine funding streams that bias research outcomes in favor of maintaining the drug’s market dominance. This omission is not accidental; it is a strategic silence designed to keep the public unaware of the true scale of hepatic damage. Do not be fooled by the bland language; the underlying agenda is to downplay risk and keep the supply chain flowing. Reject the sanitized version presented here and demand full transparency regarding adverse event reporting.
Hannah Seo
May 5, 2023 AT 00:00For anyone considering Primaquine, keep these practical steps in mind: schedule baseline liver tests before starting therapy; repeat them at regular intervals as your provider advises; avoid alcohol and other hepatotoxic substances while on the medication; and immediately report any signs such as dark urine or yellowing of the skin. Staying proactive and communicating openly with your healthcare team can greatly reduce the chance of serious liver issues.