Angioedema: What It Is, Why It Happens, and How to Treat It
When dealing with angioedema, a sudden, often painful swelling of the deeper layers of the skin and mucous membranes, you need more than a vague definition. Also called hereditary angioedema, a genetic disorder caused by C1‑esterase inhibitor deficiency, the condition can appear after a sting, a medication, or for no obvious reason at all. Angioedema encompasses rapid swelling of deeper skin layers, while hives cover the surface; this distinction helps doctors decide whether antihistamines or more targeted therapies are needed. Triggers such as ACE inhibitors, foods, or stress often require a different management plan, and recognizing that ACE‑inhibitor‑induced angioedema demands immediate drug discontinuation can be lifesaving.
Key Factors and Common Connections
Understanding angioedema means linking several related entities. Allergic reactions, immune responses that release histamine and other mediators frequently kick off swelling, but not every episode is allergy‑driven. Hereditary angioedema requires C1‑esterase inhibitor replacement, and it illustrates how a genetic deficiency can mimic an allergic flare. Meanwhile, ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema, a drug‑related swelling that occurs without histamine involvement shows that medications can bypass the typical allergy pathway entirely. The condition often demands rapid assessment: doctors must differentiate between histamine‑mediated and bradykinin‑mediated forms, because the treatment—antihistamines versus icatibant or plasma‑derived C1‑inhibitor—depends on the underlying mechanism. Early recognition also reduces the risk of airway compromise, which is the most serious complication. In short, angioedema requires a clear link between triggers, type of mediator, and appropriate therapy.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive into each of these angles. From buying cheap generic medications safely to practical comparisons of antibiotics, the posts also touch on related health topics like skin inflammation, infection risks, and hormone‑related concerns. Whether you’re looking for advice on managing a sudden swelling episode, understanding hereditary forms, or simply want to avoid medication‑induced attacks, the collection offers actionable insights you can apply today. Let’s explore the resources and give you the confidence to handle angioedema effectively.
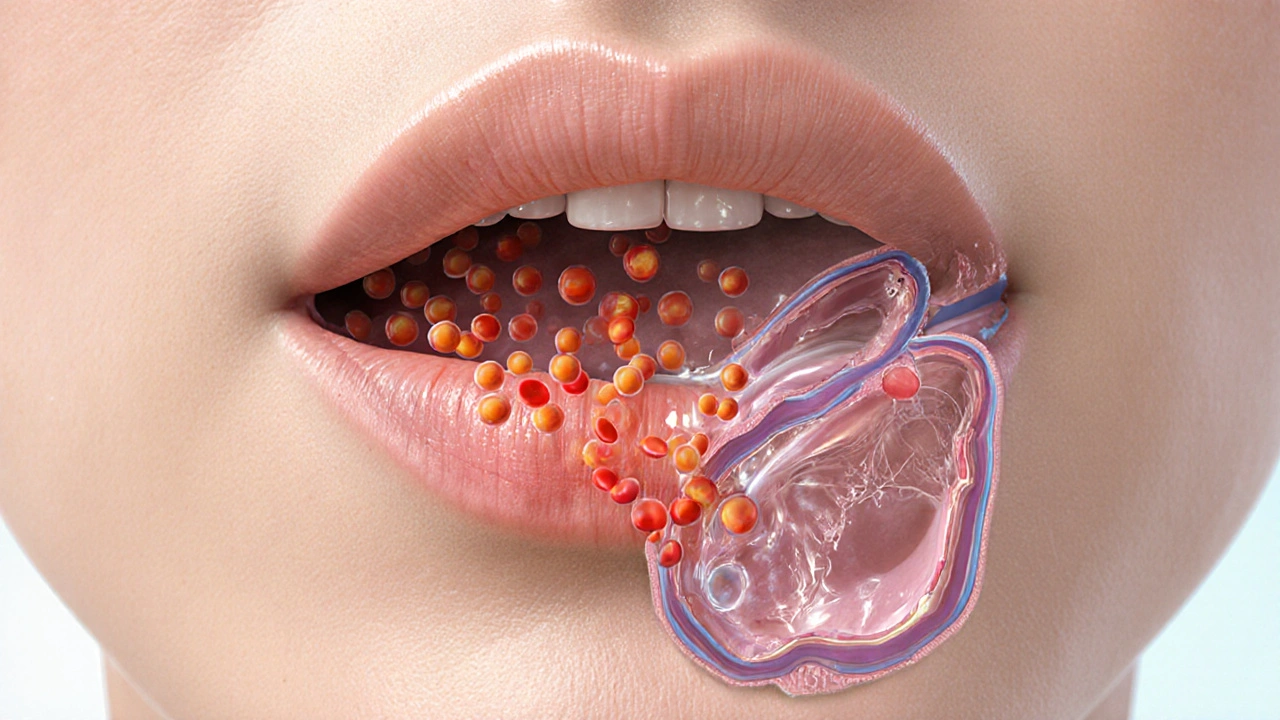
How Histamine Triggers Angioedema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Learn how histamine triggers angioedema, how to spot it, and the best treatments. Get clear differences from bradykinin‑mediated swelling and practical prevention tips.
Categories
- Medications (70)
- Health and Medicine (61)
- Health and Wellness (36)
- Online Pharmacy Guides (16)
- Nutrition and Supplements (9)
- Parenting and Family (3)
- Environment and Conservation (2)
- healthcare (2)
- prescription savings (1)