Inflammation Causes: What Triggers the Body’s Red Flag?
When working with inflammation causes, the factors that set off the body’s inflammatory response. Also known as inflammatory triggers, it can arise from tissue injury, microbial invasion, or an overactive immune system. Understanding inflammation causes helps you spot the early signs before swelling turns painful. In simple terms, inflammation causes encompass infection triggers (pathogen → immune activation), chemical irritants (toxins → cellular stress), and chronic conditions (auto‑immune → persistent inflammation). The body’s immune response influences these triggers, while lifestyle factors such as diet or stress can amplify the reaction. Recognizing these links lets you intervene early, whether by treating an infection, reducing exposure to irritants, or supporting the immune system with balanced nutrition.
Key Triggers to Watch
One of the most common culprits is infection, the invasion of bacteria, viruses, or fungi that sparks a defensive cascade. Infections act like a fire alarm: once a pathogen breaches the skin or mucosa, immune cells release cytokines, attracting more defenders and causing redness, heat, and swelling. Bacterial infections often produce stronger localized inflammation than viral ones, but both can lead to systemic symptoms if untreated. For example, a simple cut can invite Staphylococcus aureus, triggering a rapid inflammatory bout that protects the wound but also creates pain and pus. Knowing that infection → inflammation helps you choose the right treatment—antibiotics for bacterial cases, rest and hydration for viral ones—while avoiding unnecessary medication.
Another powerful driver is histamine, a compound released by mast cells that widens blood vessels and draws fluid into tissues. Histamine release contributes to allergy‑related swelling, hives, and even angioedema, a deeper form of inflammation. When an allergen binds to IgE antibodies, mast cells dump histamine, creating the classic itchy, red, and swollen response. This chemical pathway shows how the immune response influences inflammation causes, turning a harmless exposure into a noticeable flare‑up. Antihistamines block this step, proving that targeting specific mediators can calm the overall inflammatory picture. By connecting histamine → vascular leakage, you see why over‑the‑counter relief works for many everyday flare‑ups.
Putting these pieces together, you’ll notice a pattern: infection introduces foreign invaders, histamine amplifies the vascular response, and the broader immune system ties everything together. Below, you’ll find articles that dive deeper into each trigger, compare antibiotics, explain how mast cells work, and offer practical tips for keeping inflammation in check. Whether you’re dealing with a minor cut, seasonal allergies, or a chronic condition, the collection ahead gives you the facts and tools to manage inflammation causes effectively.
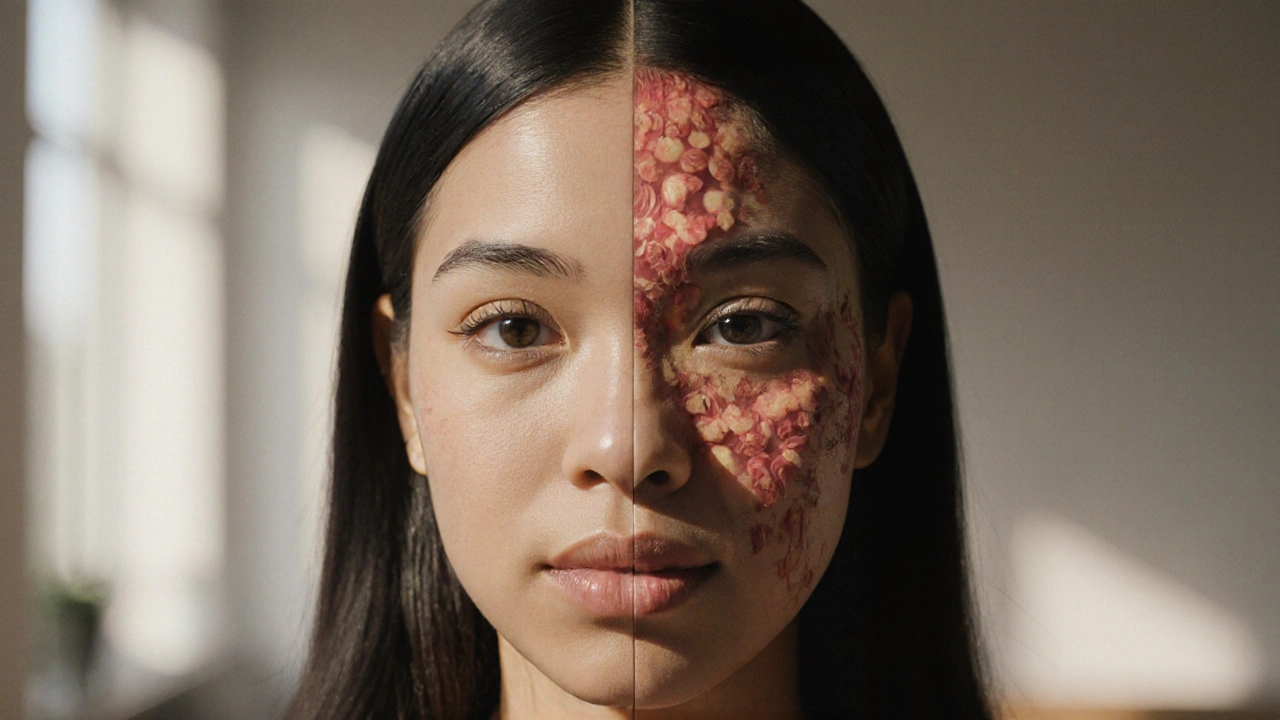

Skin Inflammation & Aging: Essential Facts & Tips
Learn how skin inflammation speeds up aging, discover top triggers, and get practical tips to calm inflammation for younger‑looking skin.
Categories
- Medications (75)
- Health and Medicine (62)
- Health and Wellness (38)
- Online Pharmacy Guides (16)
- Nutrition and Supplements (9)
- Parenting and Family (3)
- Environment and Conservation (2)
- healthcare (2)
- prescription savings (1)