Canagliflozin and the Elderly: Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Understanding Canagliflozin and Its Role in Diabetes Management
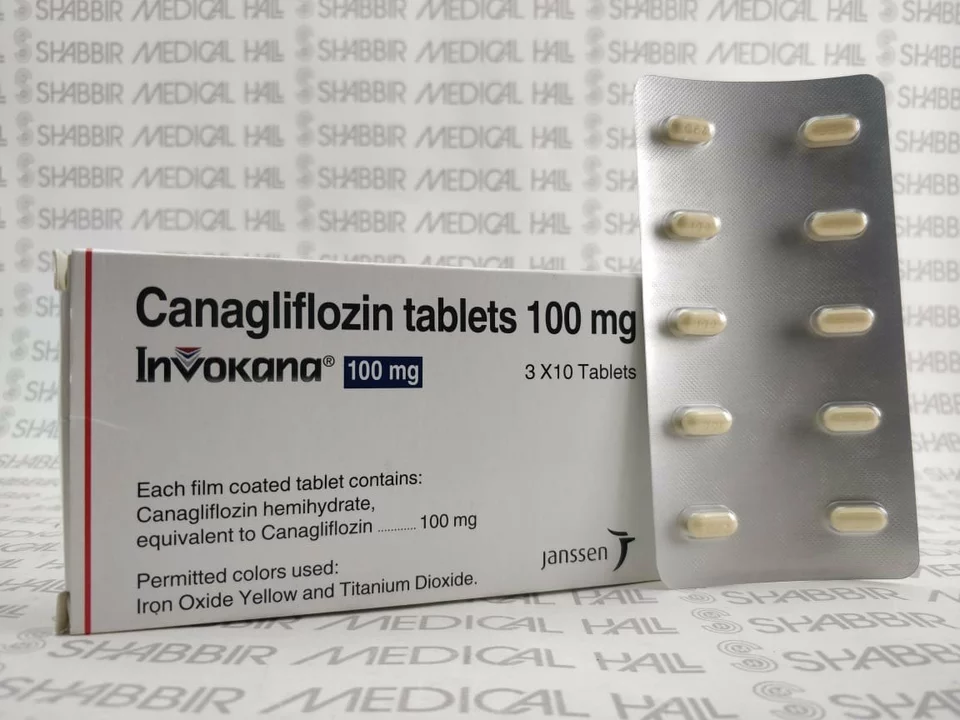
As a blogger who is passionate about sharing important health information, I feel it is necessary to discuss canagliflozin and its implications for the elderly population. Canagliflozin is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It falls under the class of drugs known as sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which work to lower blood sugar levels by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the blood. This results in the excess glucose being excreted through the urine. In this article, I will delve into the safety and efficacy of canagliflozin for older adults, along with other considerations to keep in mind.
Canagliflozin's Efficacy in Lowering Blood Sugar for Older Adults
For older adults with type 2 diabetes, maintaining optimal blood sugar control is crucial in preventing complications and improving overall health. Canagliflozin has been shown to be effective in reducing blood glucose levels in older adults. Studies suggest that canagliflozin not only lowers blood sugar levels, but also has additional benefits such as reducing body weight and blood pressure. These factors are particularly important for older adults who may be at a higher risk for heart disease and other diabetes-related complications. It is essential to note that canagliflozin should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular physical activity to achieve the best results.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Concerns for Elderly Patients
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with canagliflozin use. Some common side effects include urinary tract infections, increased urination, and genital yeast infections. While these side effects may be manageable for many older adults, it is important to weigh the potential benefits and risks of canagliflozin use. There are also some safety concerns for elderly patients taking canagliflozin, such as an increased risk for dehydration and low blood pressure due to the diuretic effect of the medication. This can be particularly concerning for older individuals who may already have issues with dehydration or low blood pressure. It is crucial to discuss these potential risks with a healthcare provider before starting canagliflozin.
Canagliflozin and Kidney Function in Elderly Patients
Because canagliflozin works through the kidneys to help eliminate excess glucose, it is essential to consider kidney function when prescribing this medication for older adults. Kidney function tends to decline with age, and many elderly individuals may already have some degree of kidney impairment. Canagliflozin may not be appropriate for individuals with significant kidney dysfunction, as it may not work effectively and could potentially worsen kidney function. Healthcare providers should closely monitor kidney function in elderly patients taking canagliflozin and adjust the medication dosage as needed.
Drug Interactions and Dosing Considerations
Older adults often take multiple medications, which can increase the risk of drug interactions. It is important to discuss all current medications with a healthcare provider before starting canagliflozin to ensure that it is safe and appropriate. Some medications, such as diuretics, may interact with canagliflozin and increase the risk of dehydration and low blood pressure. Additionally, dosing considerations should be taken into account for elderly patients, as they may require a lower dose of canagliflozin due to age-related changes in kidney function or other factors.
Managing Hypoglycemia in Older Adults Taking Canagliflozin
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can be a significant concern for older adults with diabetes. While canagliflozin has a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia compared to some other diabetes medications, it is still important to be vigilant in monitoring blood sugar levels and recognizing the signs of hypoglycemia. Older adults should work closely with their healthcare team to develop a plan for managing hypoglycemia, including regular blood sugar monitoring, recognizing the symptoms of low blood sugar, and knowing how to treat it promptly.
Discussing Canagliflozin with a Healthcare Provider
If you or a loved one is an older adult with type 2 diabetes, it is essential to have a conversation with a healthcare provider about whether canagliflozin may be an appropriate treatment option. This discussion should include a thorough evaluation of potential benefits, risks, and individual factors such as kidney function, other medications, and overall health status. By working together with a healthcare provider, older adults can make informed decisions about their diabetes management and achieve the best possible health outcomes.




Victoria Unikel
April 30, 2023 AT 01:09I’m scared that the dehydration risk will hit my dad hard.
Lindsey Crowe
April 30, 2023 AT 17:49Wow, another generic rundown of SGLT2 inhibitors. It’s like reading the same brochure over and over, only with a sprinkle of “remember to talk to your doctor” at the end. Nothing groundbreaking here, just the usual cautionary tale about kidneys and pee.
Rama Hoetzlein
May 1, 2023 AT 10:29Ah, the dance of molecules and mortality! Canagliflozin, you say? A modest chemical that pretends to be a superhero by shooing glucose out of the bloodstream, yet you hide a ferocious thirst‑inducing spirit behind that polite façade. Every dose is a gamble, a roulette wheel spinning in the kidneys of the frail, where the stakes are not just numbers on a lab report but the very essence of hydration.
Do you not see, dear readers, that the promise of lower A1c is shackled to the peril of an insidious diuresis? One sip of water becomes a daily quest, a pilgrimage through the desert of the urinary tract. And what of the yeast that thrives in the warm, moist corridors of the genitalia? It is a silent rebellion, a fungal uprising that mocks the clinician’s optimism.
The elderly, already walking a tightrope of comorbidities, are now invited to tango with a drug that can tip the balance toward hypotension. Imagine a senior, once steady, now hovering on the brink of a fainting spell after a morning bathroom dash. The pharmacist’s label cannot convey the drama of that moment.
Consider also the kidneys, those ancient filters that have seen decades of wear. Their glomerular filtration rate is a fragile tapestry, easily torn by aggressive glucose siphoning. The very mechanism that expels sugar becomes a double‑edged sword, potentially accelerating renal decline.
And let us not forget the pharmaco‑economic shackles: multiple medications, each with its own set of interactions, create a labyrinth where a single misstep can unleash a cascade of adverse events. The diuretic companion, the ACE inhibitor, the beta‑blocker-all these can conspire with canagliflozin to drain the life‑force of an older adult.
In short, my dear epistemic wanderers, treat this drug not as a panacea but as a complex character in a tragic play, demanding respect, vigilance, and perhaps most importantly, a candid conversation with the caregiver. 🌪️🤔
Lorena Garcia
May 2, 2023 AT 03:09That was a vivid portrait, Rama. While the risks you outlined are real, many older patients do benefit from the modest weight loss and blood pressure dip, as long as they’re monitored closely. It’s all about balancing the pros and cons with their individual health profile.
Dietra Jones
May 2, 2023 AT 19:49Just a heads up – spelling “dehydration” not “dehydratione”. Also, “kidney function” is usually singular when we talk about it in general. Small edits, but they help the article look sharper.
Victoria Guldenstern
May 3, 2023 AT 12:29Ah, the lofty promises of pharma wrapped in clinical jargon, yet the reality remains a modestly helpful adjunct. While the drug can shave a few points off HbA1c, the side‑effects linger like an unwanted guest at a polite dinner. The nuance, as always, is in the patient‑specific calculus.
Bill Bolmeier
May 4, 2023 AT 05:09Great points all around! For anyone nervous about the diuretic effect, staying on top of fluid intake and checking blood pressure regularly can make a world of difference. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey!
Darius Reed
May 4, 2023 AT 21:49Totally feel you, Bill! Adding a splash of electrolytes to that water can keep the cramps at bay. Also, a gentle walk after meals helps keep the sugar in check without over‑loading the kidneys.
Karen Richardson
May 5, 2023 AT 14:29From a grammatical standpoint, the phrase “canagliflozin may not be appropriate” should be followed by a comma when introducing a subordinate clause. Also, “lower” not “lowering” when describing the effect on blood pressure.
AnGeL Zamorano Orozco
May 6, 2023 AT 07:09Listen up, folks! This isn’t some sweet‑sounding bedtime story; it’s a high‑stakes drama where the hero’s cape is made of sugar‑flush magic, and the villain is dehydration, lurking like a thief in the night. If you think a tiny pill can solve everything, you’re living in a fantasy novel. The reality? You’ll be up at 3 am, staring at the bathroom tiles, wondering why your grandma is suddenly a walking water‑works. And don’t even get me started on the genital yeast – it’s a party you never invited! So before you jump on the canagliflozin hype train, ask yourself if you’re ready for the full‑blown sequel full of side‑effects and doctor visits. 🎭
Cynthia Petersen
May 6, 2023 AT 23:49Wow, that was dramatic! In truth, the drug’s benefits can outweigh the inconveniences for many, provided we keep a close eye on hydration and kidney labs. A balanced view is always best.
Marcia Hayes
May 7, 2023 AT 16:29Keeping an eye on labs is key – stay hydrated and stay positive!
Danielle de Oliveira Rosa
May 8, 2023 AT 09:09Philosophically speaking, the decision to employ canagliflozin reflects a broader societal tension between medical advancement and the stewardship of bodily autonomy. Each patient must weigh the promise of improved glycaemic control against the specter of iatrogenic complications, a dialectic as old as medicine itself.
Tarun Rajput
May 9, 2023 AT 01:49From an analytical perspective, the literature indicates that canagliflozin reduces cardiovascular events in patients with established disease, but the magnitude of this benefit diminishes with advancing age and impaired renal function. Consequently, a comprehensive assessment encompassing eGFR, comorbidities, and patient preferences is indispensable before initiating therapy.
Joe Evans
May 9, 2023 AT 18:29Great discussion, everyone! 😊 Remember to consult your healthcare provider, stay hydrated, and keep monitoring! 👍
Colin Boyd
May 10, 2023 AT 11:09While the enthusiasm is commendable, one must not overlook that the evidence base for canagliflozin in the frail elderly is still limited and that off‑label extrapolations can be perilous.
John Petter
May 11, 2023 AT 03:49Aren’t we all just chasing the next miracle pill?
Annie Tian
May 11, 2023 AT 20:29Stay hopeful! With proper monitoring, many seniors thrive on canagliflozin, enjoying better glucose control and a lighter step. Keep the dialogue open with your doctor!
April Knof
May 12, 2023 AT 13:09From a cultural standpoint, it’s interesting how different regions weigh medication risks versus lifestyle interventions, reflecting deeper values about autonomy and communal health.